Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue consisting of multiple layers of epithelial cells which can contract and expand. There are different types of epithelium cells. There’s simple squamous epithelium, which allows things to pass through it:
There is cuboidal epithelium which is used to absorb:
There is simple columnar epithelium which absorbs and secretes mucus and enzymes:
There is pseudostratified columnar epithelium which secretes mucus and moves mucus:
There is stratified squamous epithelium which protects against abrasion:
There is stratified cuboidal epithelium which is protective tissue:
There is stratified columnar epithelium which secretes and protects:
Last, there is transitional epithelium which allows the urinary organs to expand and stretch:
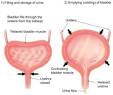
This is the type of epithelium that we are focused on. There is It is so named because of this function in the transition of degree of distension. This tissue structure type is found in urothelium, including that of the urinary bladder, the ureters, and the superior urethra and gland ducts of the prostate. When the bladder is empty, it looks like an inverted pyramid but when it’s full, it’s shaped like an oval:
The reason for this is because the bladder is made of epithelial cells which can contract and expand, as said before.
In the base of the bladder, there’s a structure called a trigone, which is the triangular area made up of the openings from the ureters and the opening into the urethra.